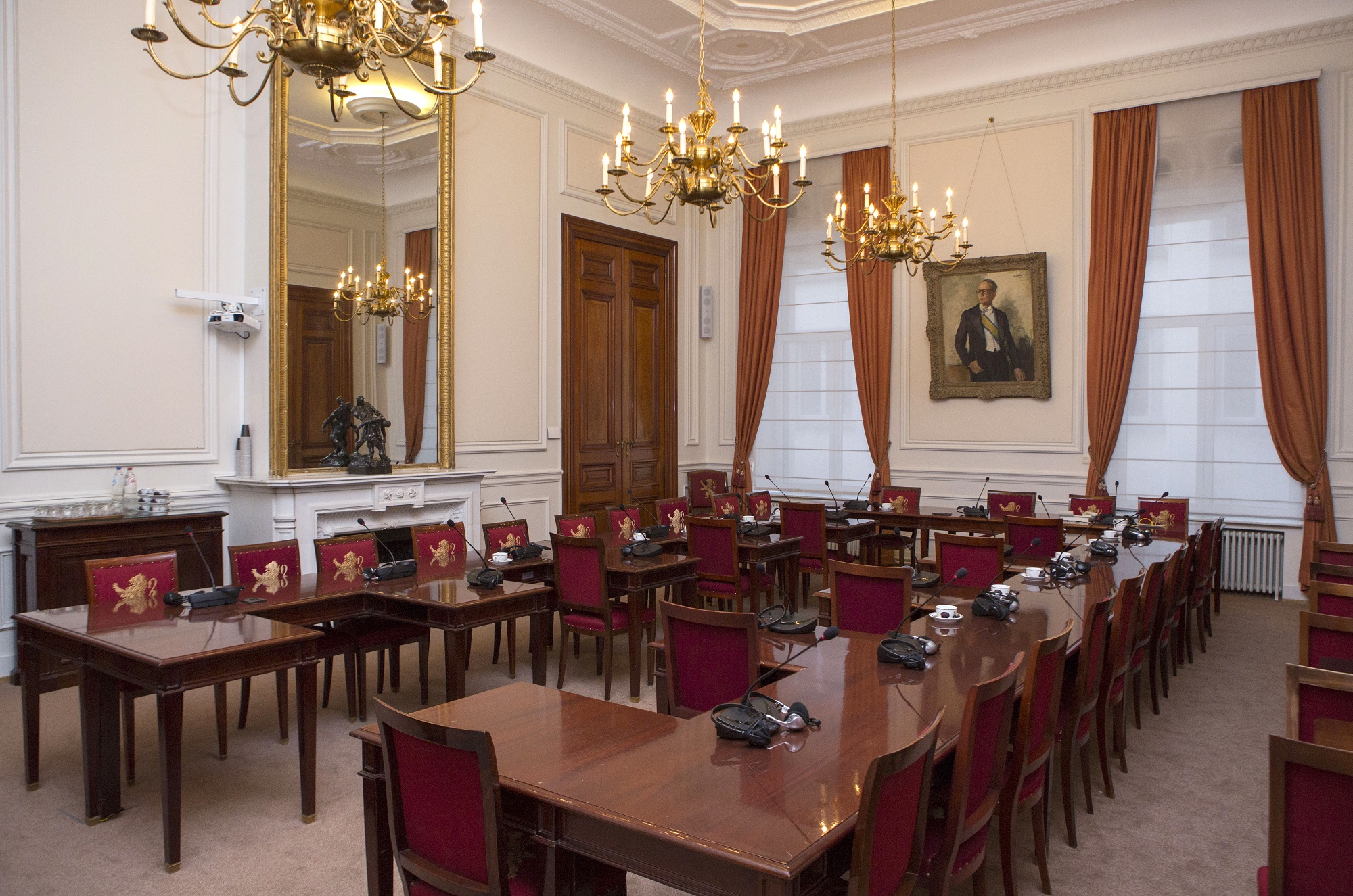
The standing committees mainly work on legislative proposals, draft resolutions and information reports, and do the bulk of the preparatory work for those texts.
The Senate has three standing committees consisting, in principle, of 20 senators appointed by the various political groups on the basis of the political balance of power in the Senate.
The committees examine the draft bills, proposals and any other matters referred to them by the plenary session of the Senate. When the work of the committee has been completed, the plenary session may discuss the outcome of that work and, if necessary, vote on the proposals adopted by the committee.
The committees can also seek advice from organizations and experts from outside the parliament, or arrange hearings and seminars.
The work carried out in the drafting of information reports on ‘transversal matters’ are becoming increasingly important. These are issues that have interfaces with the powers of various policy levels (Federal State, Communities and Regions).
The Senate also has two advisory committees: one works on equal opportunities for women and men, and the other monitors European affairs.
- Committees and working groups in the Senate: in French - in Dutch
- The Information reports of the Senate: in French - in Dutch
© Belgian Senate

